Business
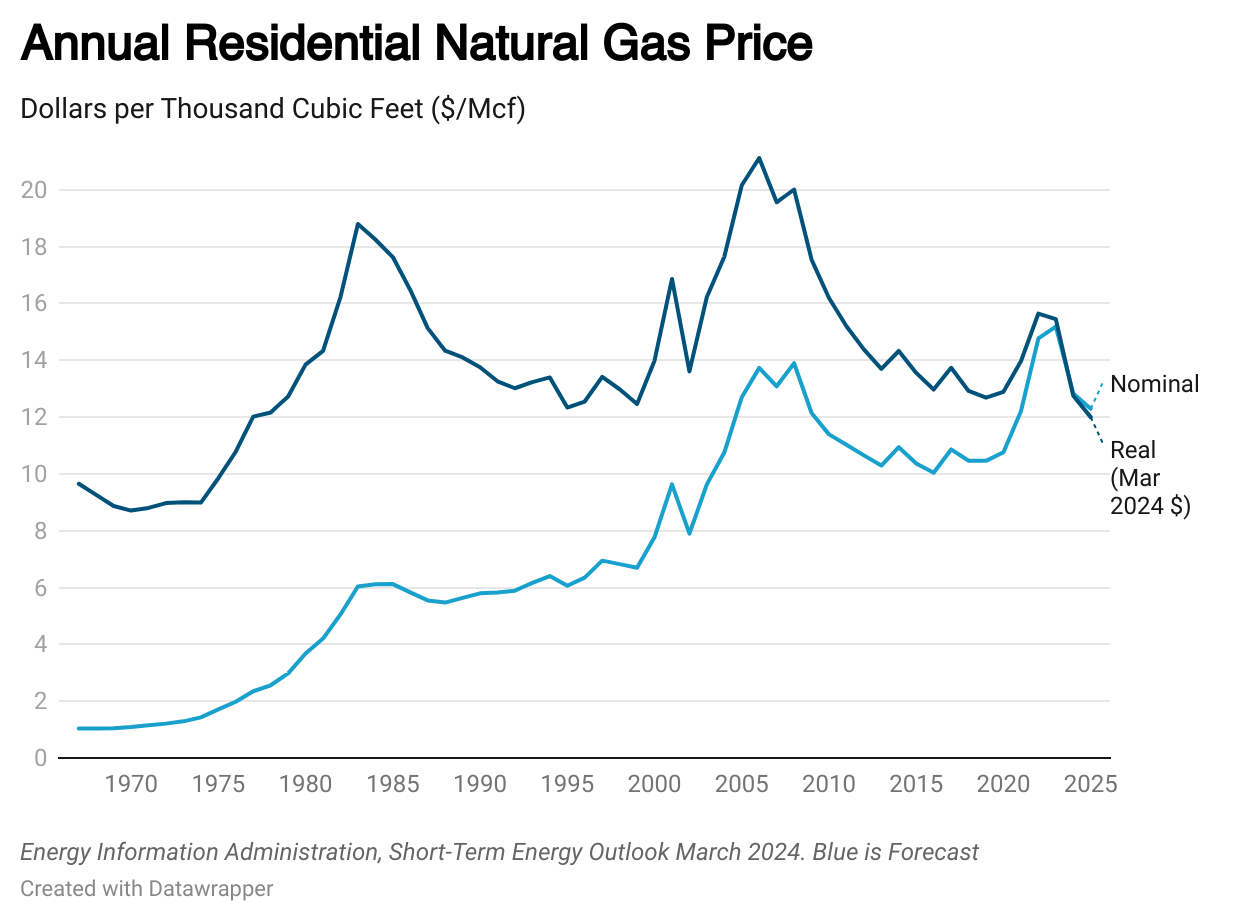
Natural Gas Prices Forecast: What to Expect This Year
Business
HRMS Globex: Top Benefits for Modern Businesses
Business
Remote Bookkeeping Jobs: How to Get Hired Fast
Business
Ironmartonline Reviews That Will Save You Time and Money

Ironmartonline Reviews That Will Save You Time and Money
Finding reliable heavy equipment online can be a challenge. With so many marketplaces and online dealers, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed or uncertain about where to invest your time and money. That’s why Ironmartonline reviews have become increasingly valuable for both buyers and sellers. This platform specializes in connecting individuals and businesses with industrial machinery, construction equipment, and specialized tools, and understanding how it works before diving in can make all the difference.
Whether you are a contractor looking to expand your fleet, a business owner seeking equipment for production, or a collector of industrial machinery, knowing the ins and outs of Ironmartonline is essential. In this article, we will explore the platform’s features, user experiences, and tips for maximizing your investment. These insights are based on real user experiences, observed trends, and practical considerations.
What is Ironmartonline?
Ironmartonline is an online marketplace specifically designed for heavy equipment and industrial machinery. Unlike general-purpose marketplaces, it focuses on connecting sellers with buyers who are serious about purchasing trucks, trailers, construction equipment, and other large-scale tools. The platform offers detailed listings, high-quality images, and tools to manage transactions effectively.
For many users, Ironmartonline offers a way to save time by avoiding traditional dealership visits and an opportunity to save money through competitive pricing and access to a wide variety of sellers in one place. Additionally, the platform’s structured approach helps users compare equipment specifications, understand market prices, and make informed decisions.
Why Users Look for Ironmartonline Reviews
Before investing in heavy equipment, buyers want transparency and assurance. That’s why Ironmartonline reviews are often consulted before making a decision. People want to know:
- Is the platform legitimate and trustworthy?
- How accurate are the listings and equipment descriptions?
- Are there hidden fees or challenges when dealing with brokers?
- Does Ironmartonline offer customer support that actually helps?
Many reviews highlight positive experiences where users saved both time and money by finding the exact equipment they needed without having to visit multiple sellers physically. Conversely, some reviews caution about potential challenges such as understanding broker fees or waiting times for niche equipment.
Key Features Highlighted in Ironmartonline Reviews
Based on user feedback and expert observations, several features make Ironmartonline stand out. Here’s a breakdown:
Extensive Equipment Listings
One of the most praised aspects of Ironmartonline is the sheer variety of equipment available. From construction vehicles to industrial machinery, the platform allows users to explore multiple categories efficiently. Buyers can compare different models, see detailed specifications, and view images to ensure they know exactly what they are purchasing.
Transparent Pricing and Bidding Options
Ironmartonline provides clear pricing information and sometimes even allows bidding on certain listings. This transparency helps buyers avoid overpaying while giving sellers a fair platform to present their equipment. Reviews frequently mention that this feature simplifies the negotiation process, reducing time spent in discussions or back-and-forth communications.
User-Friendly Interface
The platform’s interface is designed to be intuitive. Users can filter by equipment type, location, price range, and condition, which makes searching fast and efficient. Reviews often praise the clean design and easy navigation, noting that even first-time users can quickly understand how to browse, shortlist, and purchase items.
Secure Payment and Transaction Support
Security is a primary concern when dealing with expensive industrial equipment. Ironmartonline ensures that payments are processed securely, and buyers and sellers are guided through proper transaction procedures. According to multiple Ironmartonline reviews, this reduces the risk of fraud and increases confidence in each deal.
Seller and Buyer Support
Another feature highlighted repeatedly is the support provided by the platform. Customer service helps resolve disputes, answer questions about listings, and guide users through shipping logistics. This level of service is particularly appreciated by international buyers or first-time users who may not be familiar with the equipment buying process.
Detailed Equipment Descriptions
Accurate descriptions are crucial when buying heavy machinery online. Many Ironmartonline reviews note that sellers on the platform often provide comprehensive specifications, including year of manufacture, hours of use, maintenance history, and any modifications. This attention to detail helps buyers make informed choices without physical inspection.
Opportunity for Cost Savings
One of the most consistent points in reviews is the potential for savings. By aggregating multiple sellers in one marketplace, Ironmartonline allows users to compare prices and find competitive deals. Additionally, the transparency in fees ensures that buyers know exactly what they are paying for, reducing hidden costs.
Broker Services for Specialized Equipment
Some transactions involve brokers who assist in connecting buyers with sellers, particularly for rare or high-value machinery. Reviews suggest that while broker fees exist, the service often saves considerable time, especially when sourcing specialized equipment that might be difficult to locate elsewhere.
Pros and Cons Summarized from User Experiences
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Wide range of industrial equipment | Broker fees may not always be clear initially |
| Detailed listings with accurate specifications | Niche equipment may take longer to sell |
| User-friendly platform and easy navigation | Some delays in international shipping |
| Secure payment and transaction guidance | Limited independent third-party reviews |
| Responsive customer support | Waiting times can vary during peak seasons |
Tips for Using Ironmartonline Efficiently
-
Verify Listings Thoroughly: Always check descriptions and images carefully.
-
Clarify Fees Early: Understand broker or platform fees before committing.
-
Compare Multiple Options: Take advantage of the extensive listings to find competitive deals.
-
Use Secure Payment Methods: Protect yourself by using reliable payment options.
-
Engage with Support: Don’t hesitate to contact customer service if you have questions or concerns.
Conclusion
Ironmartonline offers a valuable solution for anyone looking to buy or sell heavy equipment online. Based on numerous Ironmartonline reviews, the platform provides detailed listings, transparent pricing, secure transactions, and responsive support, which collectively save both time and money. While there are some caveats regarding broker fees and niche equipment, informed users can navigate these effectively with careful planning.
By leveraging the features of Ironmartonline and following best practices, buyers and sellers can maximize efficiency, reduce risks, and access a wider range of equipment than traditional methods allow. If you’ve used Ironmartonline, share your experience in the comments and help others make informed decisions while exploring this growing marketplace.
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoMovierulz 2025 Explained: Risks, Safety, and Legality
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoChris Rea’s Music Career: Hits, Albums, Legacy
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoPerdita Weeks Disability: Facts, Rumors, and the Truth
-

 Celebrity2 months ago
Celebrity2 months agoMelissa Esplana: Life, Career, and Personal Story
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDoge HHS Migrant Housing Contract: What It Means Now
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoNew York Giants vs Atlanta Falcons Match Player Stats Breakdown
-
 Crypto3 months ago
Crypto3 months agoCrypto30x.com Review: Is This Platform Worth It?
-

 Celebrity2 months ago
Celebrity2 months agoMickey Lee: Life Story, Career, and Personal Insights





